The types of flocculants, in other words industrial polyacrylamides, are cationic, anionic or nonionic polyacrylamides. Kemira’s polyacrylamides of wide range of charge and molecular weight are sold in dry powder or emulsion format and have excellent performance. Polyacrylamides always require specific dissolution equipment to ensure that the polymer is properly dissolved in water.
Biomass balanced polymers
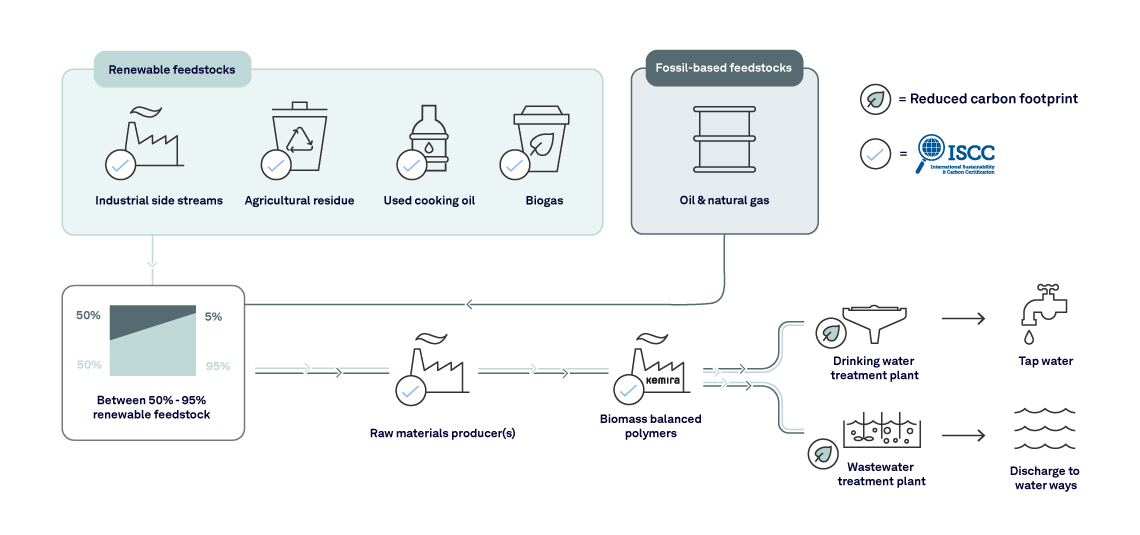
Kemira is the first chemical supplier to offer a range of biobased polymers, in the Industrial polyacrylamides product line, helping customers to make their processes more sustainable, without any compromise in performance. This novel product line is manufactured according to the principles of biomass balance, in which the majority of fossil based raw materials are replaced by ISCC Plus certified biobased and renewable mass-balanced feedstocks.
The ISCC – International Sustainability and Carbon Certification (ISCC) is one of the world’s leading certification schemes, providing solutions for the implementation and certification of sustainable and traceable supply chains. It covers all sustainable feedstocks, including agricultural and forestry biomass, circular and bio-based materials and renewables.
Sludge dewatering polymer dosage
Sludge conditioning is one of the key applications for flocculants. The amount of sludge sent for disposal or reuse is an important cost driver for a wastewater treatment plant. Improving the running conditions for the dewatering unit and the accurate dosage of appropriate polymers for sludge dewatering can lead to a considerable increase in sludge dryness and decreased sludge volumes, lowering sludge handling costs and minimizing the impact on the environment.
Digested sludges with a high pre-precipitated primary sludge content typically need lower polymer dosages and charge densities than sludges that are rich in biological sludge from secondary treatment. The polymer dosage is commonly based on the active polymer content of the made-up polymer solution and on the dry-solids (DS) content of the sludge. The dosage for an average cationic PAM for digested wastewater sludge can range from 5 to 15 kg active polymer per tonne DS [kg/t DS]. But dosages far above and below are also often reported due to local circumstances and sludge composition.
Our polymer products for water and sludge applications are sold under the following brand names:
Cationic flocculants
Cationic polyacrylamides are used, among other things, for the dewatering of sludge from biological treatment processes. Typically, the higher the share of biological sludge in the total amount of sludge, the higher the cationic charge density required in the polymer.
Kemira produces a full range of cationic dry powder flocculants / polyacrylamides (CDPAM) in a range of molecular weights. We also offer a full range of cationic inverse emulsion (CEPAM) flocculants of different cationic charge densities and molecular weight variants. Polymers in emulsion form typically have faster make-up times, as well as additional flexibility in molecular architecture optimization. The most recent addition to the CEPAM portfolio is called Kemira Superfloc® 7000 series.
Anionic flocculants
Anionic polyacrylamides are used, among other things, for water clarification and process water recycling. Anionic polyacrylamides are easier to polymerize to very high molecular weights. We produce anionic powder flocculants / polyacrylamides (ADPAM) with anionic charge density ranging from 0-100%. We also offer anionic inverse emulsion (AEPAM) flocculants in a standard range plus in extremely high molecular weight via Kemira’s proprietary emulsion hydrolysis technology.
Nonionic flocculants
Nonionic polyacrylamides are used, among other things, in mining to improve throughput, enhance yield and optimize processes especially where low pH conditions are involved. Nonionic powder flocculants can be produced with very high molecular weights, giving it the capability to form large, rapid-settling, good-compacting flocs. We produce nonionic powder flocculants / polyacrylamides (NDPAM) in a standard range plus in high and low molecular weights.
Organic coagulants
We offer a range of liquid organic coagulants (polyamines and poly-DADMACs) of the highest industry-quality.
- Polyamines often replace or reduce the use of inorganic coagulants for turbidity reduction in process or wastewater streams. They are particularly useful in areas of biological waste processing and fermentation applications.
- Polydiallydimethyl ammonium chloride (PolyDADMAC) is often used in filtration applications or in conjunction with our flocculant products. These polymers are highly effective in many water treatment clarification processes. It can also be used in combination with our flocculant and coagulant products to lower overall treatment costs.